- 86-21-56469616
- 86-18019205509
- minstar@minstargroup.com
- Language:English
- English
Your Location:Home >Products >Pharmaceutical >128-37-0
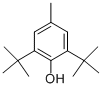

Appearance:white crystalline solid
Throughput:200|Metric Ton|Month
pd_productuse:Antioxidant 264 as general antioxidants is used widely in polymer materials, petroleum products and food processing industries. Antioxidant 264 is commonly used rubber antioxidant, heat, oxygen aging
Delivery Time:in stock
Purity:99.00%
Handling and Storage Precautions for safe handling
Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid formation of dust and aerosols.
Provide appropriate exhaust ventilation at places where dust is formed.
Normal measures for preventive fire protection.
Conditions for safe storage
Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place.Keep in a dry place.
Fire-fighting Measures
Suitable extinguishing media
Use water spray, alcohol-resistant foam, dry chemical or carbon dioxide.
Special protective equipment for fire-fighters
Wear self contained breathing apparatus for fire fighting if necessary.
Chemical Properties white crystalline solid
Uses Antioxidant 264 as general antioxidants is used widely in polymer materials, petroleum products and food processing industries. Antioxidant 264 is commonly used rubber antioxidant, heat, oxygen aging have some protective effect, but also can inhibit copper harm. This product does not change color, not pollution. Antioxidants 264 high solubility in oil, no precipitation, less volatile, non-toxic and non-corrosive.
General Description White crystalline solid.
Air & Water Reactions Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile Phenols, such as 2,6-Di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol, do not behave as organic alcohols, as one might guess from the presence of a hydroxyl (-OH) group in their structure. Instead, they react as weak organic acids. Phenols and cresols are much weaker as acids than common carboxylic acids (phenol has Ka = 1.3 x 10^[-10]). These materials are incompatible with strong reducing substances such as hydrides, nitrides, alkali metals, and sulfides. Flammable gas (H2) is often generated, and the heat of the reaction may ignite the gas. Heat is also generated by the acid-base reaction between phenols and bases. Such heating may initiate polymerization of the organic compound. Phenols are sulfonated very readily (for example, by concentrated sulfuric acid at room temperature). The reactions generate heat. Phenols are also nitrated very rapidly, even by dilute nitric acid. Nitrated phenols often explode when heated. Many of them form metal salts that tend toward detonation by rather mild shock. May react with oxidizing materials.
Fire Hazard 2,6-Di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol is combustible.
CAS:885523-08-0
CAS:517920-73-9
CAS:400-53-3
CAS:53135-24-3