Your Location:Home > Products > Pharmaceutical > 5-Aminolevulinic acid phosphate
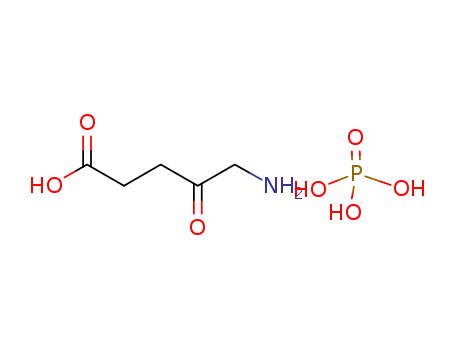

CasNo: 868074-65-1
Molecular Formula: C5H9NO3.H3O4P
|
868074-65-1 Name |
|
|
Name |
5-Aminolevulinic acid phosphate |
|
Synonym |
5-amino-4-oxopentanoic acid,phosphoric acid;5-aminolevulinic acid phosphate,5-ALA phosphate;5-Aminolevulinic acid phosphate;5-Amino-4-oxopentanoic acid phosphate;5-Aminolevulinic acid phosphate(ALA );Pentanoic acid, 5-amino-4-oxo-, phosphate (1:1);ALA Synonyms:5-Aminolevulinic acid phosphate;5-Aminolevulinic Acid Phosphate (5-ALA) |
|
868074-65-1 Chemical & Physical Properties |
|
|
Molecular Formula |
C5H12NO7P |
|
Molecular Weight |
229.12500 |
|
PSA |
167.96000 |
|
Exact Mass |
229.03500 |
5-Aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA), which is a precursor of heme, is the first compound produced in the heme synthetic pathway. 5-ALA is contained in various foods, including vegetables, fruits, and fermented liquors. 5-Aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA), a non-proteinogenic five-carbon amino acid, has received much attention for its wide applications in medicine and agriculture. Human adenocarcinoma cells of the line WiDr were incubated with 5-aminolevulinic acid to induce protoporphyrin IX (PpIX) and then exposed to laser light of wavelength 635 nm.
This study investigated the preventive effects of sodium ferrous citrate (SFC) and 5-aminolevulinic acid phosphate (ALA) on several metabolic dysfunctions associated with obesity because they have been shown to alleviate abnormal glucose metabolism in humans.
This study examined the efficiency of sunflower plants to remediate Cr-contaminated soils using a plant growth regulator, 5-aminolevolinic acid (ALA). EDDS augmented Cr accumulation and translocation in sunflower tissues, inhibiting plant growth and development. In contrast, ALA promoted plant growth, biomass attributes, and photosynthetic.