Your Location:Home > Products > Fine Chemicals > Hexafluorobisphenol A


CasNo: 1478-61-1
Molecular Formula: C15H10F6O2
Appearance: White to off-white powder
|
1478-61-1 Name |
|
|
Name |
Hexafluorobisphenol A |
|
Synonym |
4,4'-(HEXAFLUOROISOPROPYLIDENE)DIPHEOL;2,2-BIS(4-HYDROXYPHENYL)HEXAFLUOROPROPANE;TIMTEC-BB SBB001375;4,4'-[2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(trifluoromethyl)ethylidene]diphenol;HexafluorophenolA;BISPHENOL AF-M;BPAF;2,2-BIS(PARA-HYDROXYPHENYL)PERFLUOROPROPANE |
|
1478-61-1 Chemical & Physical Properties |
|
|
Melting point |
160-163 °C(lit.) |
|
Boiling point |
344.1±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
|
Density |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|
Molecular Formula |
C15H10F6O2 |
|
Molecular Weight |
336.229 |
|
Flash Point |
161.9±27.9 °C |
|
PSA |
40.46000 |
|
LogP |
2.82 |
|
Exact Mass |
336.058502 |
|
Vapour Pressure |
0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
|
Index of Refraction |
1.506 |
Hexafluorobisphenol A, white to off-white powder, acts as an endocrine-disrupting chemical (EDC), activating estrogen through the estrogen receptor ERα. Hexafluorobisphenol A mainly is used for fluorine rubber vulcanization accelerator FF34 with fluorine rubber, vulcanized permanent deformation resistance, tensile strength is high; but also can be used as pharmaceutical intermediates.
Definition
ChEBI: An organofluorine compound that is bisphenol A with its methyl hydrogens replaced by fluorines.
Hazard
Moderately toxic by ingestion.
Flammability and Explosibility
Notclassified
InChI:InChI=1/C15H10F6O2/c1-15(2,7-3-5-8(22-20)6-4-7)9-10(16)12(18)14(23-21)13(19)11(9)17/h3-6H,1-2H3
This paper describes the synthesis and characterization of epoxy resins based on (hexafluoroisopropylidene)diphenol (EFN) and p,p’-isopropylidenebisphenol (EBN), respectively and 4, 4’- (hexafluoroisopropylidene)dipthalic-imideamine (IMAM), a curing agent. The investigation of thermal decomposition of the cured compounds by thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA) indicated the higher thermal stability of EFN and EBN resins initially with DDS and at elevated temperatures with IMAM. It was also observed that EFN resins were thermally more stable than EBN resins cured with corresponding curing agents.
The invention provides a method for manufacturing bisphenol AF. The method is a manufacturing method using hexafluoroacetone, phenol and hydrogen fluoride, is suitable for a convenient refining method, meanwhile can improve the yield and can reduce the load to the environment. A method for manufacturing 2,2-di(4-hydroxyphenyl)hexafluoropropane is characterized in that: the hexafluoroacetone and the phenol are reacted in the presence of the hydrogen fluoride, wherein when the reaction begins, based on 1 mole of phenol, the hexafluoroacetone is 0.55 to 2 moles and the hydrogen fluoride is 8 to 200 moles.
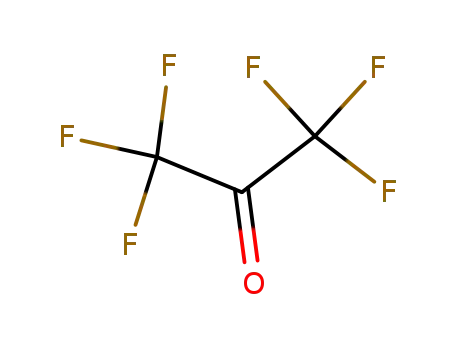
Hexafluoroacetone
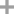
phenol

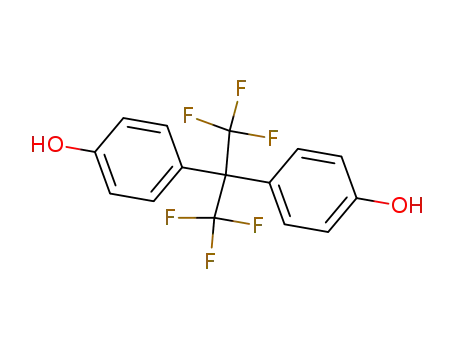
4,4'-(hexafluoroisopropylidene)diphenol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With hydrogen fluoride; In melt; at 10 - 100 ℃; for 2h; Temperature; Autoclave;
|
95% |
|
With hydrogen fluoride;
|
|
|
surface-bound sulfonic acid-containing material; at 90 ℃; for 24h;
|
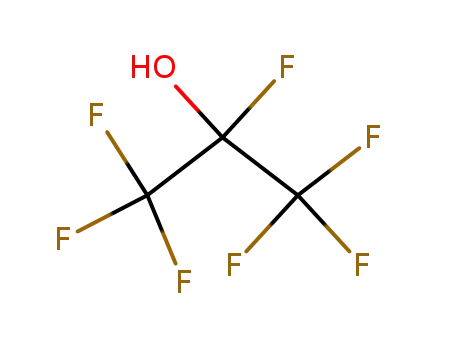
heptafluoropropan-2-ol


phenol


4,4'-(hexafluoroisopropylidene)diphenol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With hydrogen fluoride; at 110 ℃; for 6h; under 7125.71 Torr; Autoclave;
|
82% |

Hexafluoroacetone

phenol

heptafluoropropan-2-ol
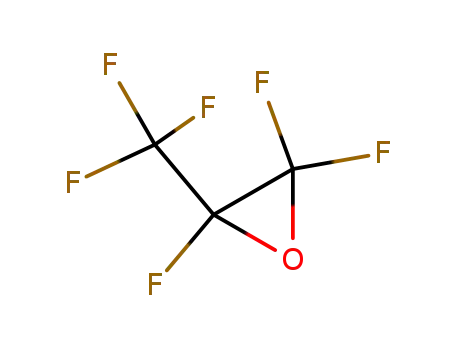
Hexafluoropropene oxide
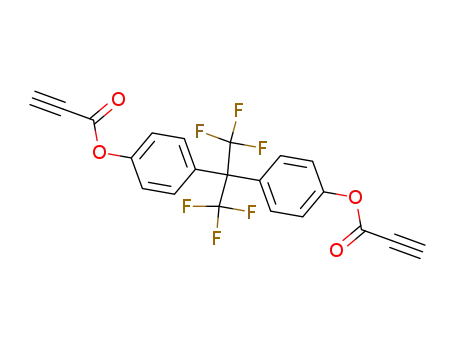
Propynoic acid 4-[2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(4-propynoyloxy-phenyl)-1-trifluoromethyl-ethyl]-phenyl ester
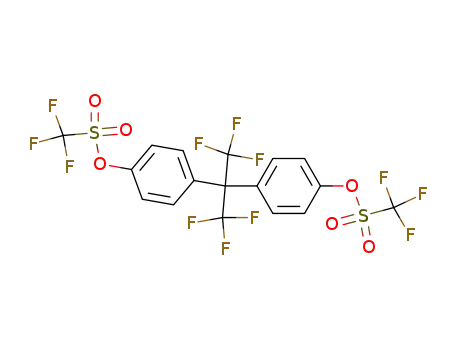
2,2-bis(4-trifluoromethanesulfonyloxyphenyl)hexafluoropropane
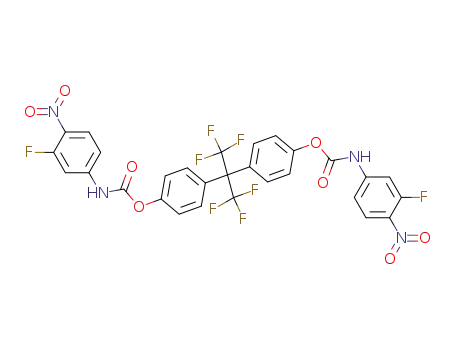
2,2-bis<(p-3'-fluoro-4'-nitrophenyl-carbamato)phenyl>-1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoropropane
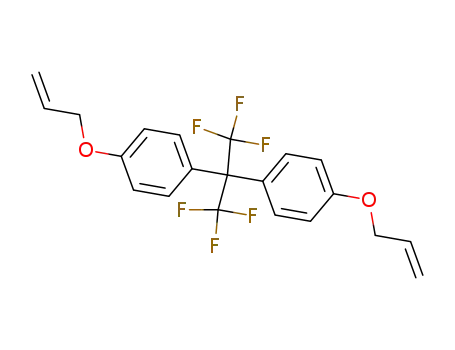
2,2-bis(4-allyloxyphenyl)hexafluoropropane